7569번: 토마토
첫 줄에는 상자의 크기를 나타내는 두 정수 M,N과 쌓아올려지는 상자의 수를 나타내는 H가 주어진다. M은 상자의 가로 칸의 수, N은 상자의 세로 칸의 수를 나타낸다. 단, 2 ≤ M ≤ 100, 2 ≤ N ≤ 100,
www.acmicpc.net
문제
철수의 토마토 농장에서는 토마토를 보관하는 큰 창고를 가지고 있다. 토마토는 아래의 그림과 같이 격자모양 상자의 칸에 하나씩 넣은 다음, 상자들을 수직으로 쌓아 올려서 창고에 보관한다.
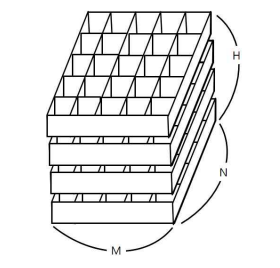
창고에 보관되는 토마토들 중에는 잘 익은 것도 있지만, 아직 익지 않은 토마토들도 있을 수 있다. 보관 후 하루가 지나면, 익은 토마토들의 인접한 곳에 있는 익지 않은 토마토들은 익은 토마토의 영향을 받아 익게 된다. 하나의 토마토에 인접한 곳은 위, 아래, 왼쪽, 오른쪽, 앞, 뒤 여섯 방향에 있는 토마토를 의미한다. 대각선 방향에 있는 토마토들에게는 영향을 주지 못하며, 토마토가 혼자 저절로 익는 경우는 없다고 가정한다. 철수는 창고에 보관된 토마토들이 며칠이 지나면 다 익게 되는지 그 최소 일수를 알고 싶어 한다.
토마토를 창고에 보관하는 격자모양의 상자들의 크기와 익은 토마토들과 익지 않은 토마토들의 정보가 주어졌을 때, 며칠이 지나면 토마토들이 모두 익는지, 그 최소 일수를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하라. 단, 상자의 일부 칸에는 토마토가 들어있지 않을 수도 있다.
입력
첫 줄에는 상자의 크기를 나타내는 두 정수 M,N과 쌓아올려지는 상자의 수를 나타내는 H가 주어진다. M은 상자의 가로 칸의 수, N은 상자의 세로 칸의 수를 나타낸다. 단, 2 ≤ M ≤ 100, 2 ≤ N ≤ 100, 1 ≤ H ≤ 100 이다. 둘째 줄부터는 가장 밑의 상자부터 가장 위의 상자까지에 저장된 토마토들의 정보가 주어진다. 즉, 둘째 줄부터 N개의 줄에는 하나의 상자에 담긴 토마토의 정보가 주어진다. 각 줄에는 상자 가로줄에 들어있는 토마토들의 상태가 M개의 정수로 주어진다. 정수 1은 익은 토마토, 정수 0 은 익지 않은 토마토, 정수 -1은 토마토가 들어있지 않은 칸을 나타낸다. 이러한 N개의 줄이 H번 반복하여 주어진다.
토마토가 하나 이상 있는 경우만 입력으로 주어진다.
출력
여러분은 토마토가 모두 익을 때까지 최소 며칠이 걸리는지를 계산해서 출력해야 한다. 만약, 저장될 때부터 모든 토마토가 익어있는 상태이면 0을 출력해야 하고, 토마토가 모두 익지는 못하는 상황이면 -1을 출력해야 한다.
나의 풀이
이 문제는 BFS를 이용해서 해결하면 됩니다. 다만 3차원 배열로 진행해야 하기 때문에 헷갈릴 수가 있습니다.
그런데 생각보다 어렵게 생각 안해도 되는게, 기존의 방식에서 위, 아래 탐색을 추가하기만 하면 됩니다.
Kotlin
import java.util.*
import kotlin.math.max
val dx = arrayOf(0, 1, 0, -1)
val dy = arrayOf(1, 0, -1, 0)
val dz = arrayOf(1, -1)
data class Box(val z: Int, val x: Int, val y: Int)
fun main() = with(System.`in`.bufferedReader()) {
val (m, n, h) = readLine().split(" ").map { it.toInt() }
val box = Array(h) { Array(n) { readLine().split(" ").map { it.toInt() }.toIntArray() } }
val tomatoes = mutableListOf<Box>()
var check = true
for (k in 0 until h) {
for (i in 0 until n) {
for (j in 0 until m) {
if (box[k][i][j] == 1) {
tomatoes.add(Box(k, i, j))
}
if (box[k][i][j] == 0) {
check = false
}
}
}
}
if (check) {
println(0)
return@with
}
bfs(n, m, h, tomatoes, box)
}
fun bfs(n: Int, m: Int, h: Int, tomatoes: MutableList<Box>, box: Array<Array<IntArray>>) {
val queue: Queue<Box> = LinkedList()
val visited = Array(h) { Array(n) { IntArray(m) } }
tomatoes.forEach {
queue.add(it)
visited[it.z][it.x][it.y] = 1
}
while (queue.isNotEmpty()) {
val (z, x, y) = queue.poll()
for (i in 0 until 2) {
val tempZ = z + dz[i]
if (tempZ in 0 until h &&
visited[tempZ][x][y] == 0 &&
box[tempZ][x][y] == 0) {
visited[tempZ][x][y] = visited[z][x][y] + 1
queue.add(Box(tempZ, x, y))
}
}
for (i in 0 until 4) {
val tempX = x + dx[i]
val tempY = y + dy[i]
if (tempX in 0 until n &&
tempY in 0 until m &&
visited[z][tempX][tempY] == 0 &&
box[z][tempX][tempY] == 0) {
visited[z][tempX][tempY] = visited[z][x][y] + 1
queue.add(Box(z, tempX, tempY))
}
}
}
var temp = 0
for (k in 0 until h) {
for (i in 0 until n) {
for (j in 0 until m) {
if (box[k][i][j] != -1 && visited[k][i][j] == 0) {
println(-1)
return
}
temp = max(temp, visited[k][i][j])
}
}
}
println(temp - 1)
}
Java
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
class box {
int z;
int x;
int y;
box(int z, int x, int y) {
this.z = z;
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
class Main {
static BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static int[] dx = {0, 1, 0 , -1};
static int[] dy = {1, 0, -1 ,0};
static int[] dz = {1, -1};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
int m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int h = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int[][][] box = new int[h][n][m];
ArrayList<box> tomatoes = new ArrayList<>();
boolean check = true;
for (int k = 0; k < h; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
box[k][i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if (box[k][i][j] == 1) {
tomatoes.add(new box(k, i, j));
}
if (box[k][i][j] == 0) {
check = false;
}
}
}
}
if (check) {
System.out.println(0);
return;
}
System.out.println(bfs(n, m, h, tomatoes, box));
}
static int bfs(int n, int m, int h, ArrayList<box> tomatoes, int[][][] box) {
Queue<box> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int[][][] visited = new int[h][n][m];
for (box tomato : tomatoes) {
queue.add(tomato);
visited[tomato.z][tomato.x][tomato.y] = 1;
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
box current = queue.poll();
int z = current.z;
int x = current.x;
int y = current.y;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
int tempZ = z + dz[i];
if (tempZ >= 0 && tempZ < h &&
visited[tempZ][x][y] == 0 &&
box[tempZ][x][y] == 0) {
visited[tempZ][x][y] = visited[z][x][y] + 1;
queue.add(new box(tempZ, x, y));
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int tempX = x + dx[i];
int tempY = y + dy[i];
if (tempX >= 0 &&
tempX < n &&
tempY >= 0 && tempY < m &&
visited[z][tempX][tempY] == 0 &&
box[z][tempX][tempY] == 0) {
visited[z][tempX][tempY] = visited[z][x][y] + 1;
queue.add(new box(z, tempX, tempY));
}
}
}
int temp = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < h; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (box[k][i][j] != -1 && visited[k][i][j] == 0) {
return -1;
}
if (temp < visited[k][i][j]) {
temp = visited[k][i][j];
}
}
}
}
return temp - 1;
}
}
'백준 > 그래프 탐색' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 4179번: 불! - Kotlin, Java (BFS) (0) | 2023.09.27 |
|---|---|
| 2636번: 치즈 - Kotlin (BFS) (0) | 2023.08.02 |
| 1967번: 트리의 지름 - Kotlin (BFS) (0) | 2023.06.11 |
| 17070번: 파이프 옮기기 1 - Kotlin (DFS) (0) | 2023.06.09 |
| 1707번: 이분 그래프 - Kotlin (BFS) (0) | 2023.06.07 |
